There are a lot of strategies and diet fads out there for those wanting to lose excess weight. One technique rising in popularity recently is intermittent fasting. While this approach to food intake control is not new, more and more people are discovering its potential advantages for shedding excess weight and improving overall health.
Below, we’ll go over what intermittent fasting entails so you can better decide if it’s right for you.
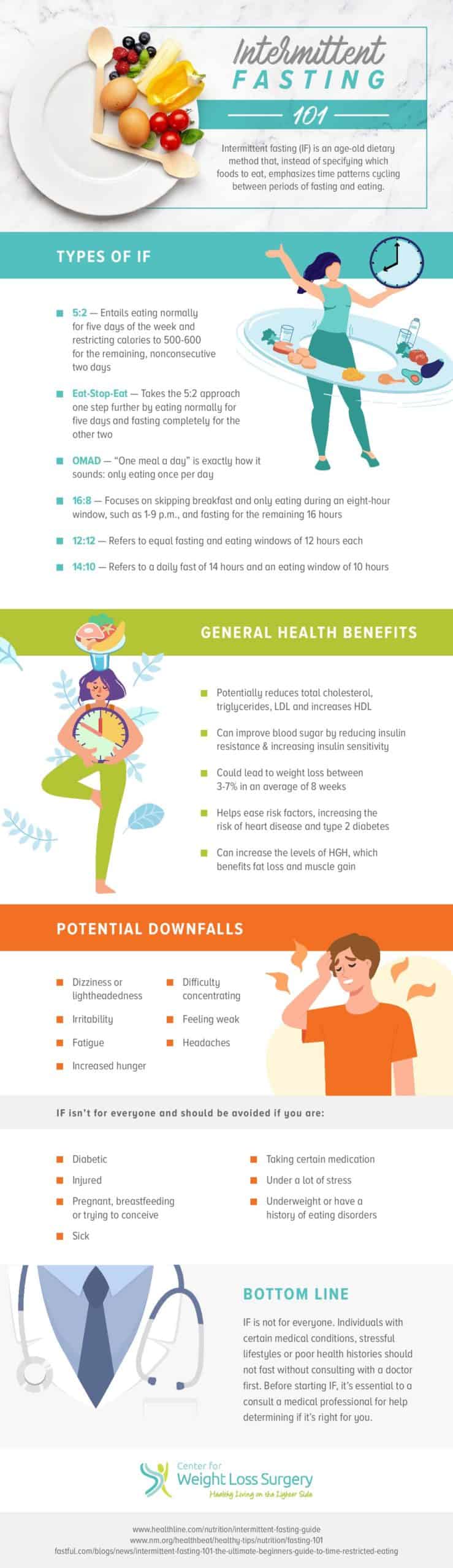
What Is Intermittent Fasting?
Intermittent fasting (IF) is not a diet specifying the foods you can and cannot eat. Instead, it is a pattern cycling between periods of intake and periods when you do not eat, i.e., fasting. Put simply, it focuses more on when you should eat and not what you should eat. As such, it isn’t so much of a diet as it is an eating pattern.
It’s important to understand that not every IF pattern follows the same outline. One of the more widespread types is OMAD, or “one meal a day.” Straightforward and easy to keep track of, OMAD is just how it sounds, with one meal being consumed each day, usually around the same time. If only eating once a day isn’t feasible, there’s the 14:10 method. This refers to a fasting window of 14 hours and an eating window of 10 hours. Once comfortable, you could take it up a notch with the 16:8, which has a 16-hour fasting window.
There are also plans based on the week rather than the day. The 5:2, for example, permits the faster to eat normally for five days a week while restricting calories to 500-600 for the other two, nonconsecutive days. Going beyond this is the “eat-stop-eat” method. It makes 5:2 more challenging by restricting the two days to no food at all.
While “eating normally” may vary by person, it’s advised to consume a range of nutritious foods and follow a healthy diet, such as the Mediterranean diet. It’s essential to avoid overeating after fasting. High-calorie junk food and fried items should also be avoided for better results. Lastly, staying hydrated is vital. Fasters should drink plenty of water and may even enjoy zero-calorie beverages, such as tea and black coffee.
What Are the Potential Benefits?
Experts have found that when the body goes hours without food, it begins to exhaust sugar stores and burn fat. This process is referred to as metabolic switching. With IF, the goal is to prolong the time period without food so the body is able to effectively burn through all of the calories from the last meal and extend the fat-burning period.
In addition to weight loss, activating this metabolic switch and staying in a state of fat burn may lead to a host of other benefits. Many people use it to address existing health conditions such as high cholesterol and irritable bowel syndrome. However, studies show it may also help protect against developing age-related neurodegenerative disorders, inflammatory bowel disease, and chronic diseases, such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
IF Is Not for Everyone
Negative side effects are possible with IF, especially for people with certain pre-existing conditions. A few potential downfalls include dizziness, headaches, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and irritability.
IF should be avoided by people who are/have:
- Under 18
- Pregnant, breastfeeding, or trying to conceive
- Taking certain medications
- A history of eating disorders
- Type 1 diabetes
It’s Important to Speak With Your Doctor
Determining whether to incorporate intermittent fasting into your lifestyle should include a discussion with your doctor. Doing so is particularly vital for those with a medical condition or history of poor health, as well as those experiencing unusual anxiety or excessive stress.
All things considered, intermittent fasting can become a sustainable way of eating and a powerful tool for staying healthy when done right and approved by a doctor. For further information on the types of intermittent fasting as well as the advantages, please see the accompanying resource.